C-command Index Definitio | Origo nominis | Notae | Nexus interniTabula navigationis
Arbores syntacticae
nodosarboribus syntacticisdominationeTanya Reinhardt1976Ronaldus Langacker1969S-nodus1972Raimundus JackendoffTanya ReinhardtMITelementorumNick Clements

Arbor syntactica c-command monstrat. Filiae se c-imperant et filia ad sinistram quoque c-imperat filiolas suae sororis.
c-command (Latine fortasse aptius c-imperatum; vide originem nominis) est coniunctio praecipua inter nodos in arboribus syntacticis. Sorores se c-imperant et materterae c-imperant filias suarum sororum.
Index
1 Definitio
2 Origo nominis
3 Notae
4 Nexus interni
Definitio |
Definitio c-imperati in dominatione fundatur. Ergo nodus A c-imperat nodum B si et tantum si:
- A non dominatur B
- B non dominatur A
- Omnes nodi qui dominantur A etiam dominantur B.[1][2]

Arbor syntactica c-command monstrans.
Exempli gratia, in arbore ad dexteram:
M nihil c-imperat.
A c-imperat B, C, D, E, F, and G.
B nihil c-imperat.
C c-imperat D, F, et G.
D c-imperat C , et E.
E, F, et G nihil c-imperat.
Origo nominis |
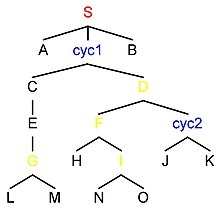
Historia command.
Verbum Anglicum command, scilicet 'ductum', ex verbo Latino commendandi deducitur, etiamsi valet potius ac imperare. Nomen, quod proposuit Tanya Reinhardt anno 1976, est abbreviatio appellationis in lingua Anglica consituent command ("imperatum elementorum"). Ronaldus Langacker anno 1969 coniunctionem paenem eandem command proposuit, qua regula 3 legitur "si S-nodus[3], qui proxime dominatur A, etiam dominat B".
Anno 1972, Raimundus Jackendoff definitionem tam emendavit ut in loco S-nodi ullus nodus cyclicus sit nodus maternus c-imperati coniunctionis. Deinde Tanya Reinhardt in sua dissertatione apud MIT prima scripsit c-command, ut command inter omnes greges elementorum? describeret. Reinhardt nomen et sententiam c-imperati Nick Clements ascripsit.
Ergo videmus in imagine ad sinistram definitionem secundum Langacker de omnibus nodis sub S tractare, secundum Jackendoff de nodis sub S, cyc1, et cyc2, et secundum Reinhardt de omnibus nodis cum plus quam uno ramo/filia scilicet sub S, cyc1, cyc2, D, F, G, et I.
Nota bene definitionem etiamsi humilius in arbore sitam, quo strictior videatur, re vera esse generaliorem:
Omnes nodi ramos saltem duos habentes possunt esse nodi materni in coniunctione c-imperati.
Notae |
↑ Haegeman, Liliane (1994). Introduction to Government and Binding Theory (2a. ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. p. 147
↑ Carnie, Andrew (2002). Syntax: A Generative Introduction (1a. ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. p. 75
↑ Illo tempore nondum floruit X-bar theoria et S-nodus, id est Sententiae nodus, fuit nodus maternus articulorum in loco T vel ConjP.
Nexus interni
- Dominatio
- k-command
- Ligatio
- m-command